34:10 Synthesis of Mechanisms has different objectives
- Function generation ⇒ Mechanical Calculators/Computers
- Path generation ⇒ Point following a path
- Motion generation ⇒ move something from position 1 to position 2
- Methods of Mechanisms Synthesis
- Graphyical Synthesis of Mechanisms
- Analytical Synthesis of Mechanisms
Can be used for:
Positional Analysis by using the given lengths of links, Extreme positions can be found graphically
Synthesis of Mechanisms to achieve desired motion (e.g. length of a link to achieve a required stroke length)
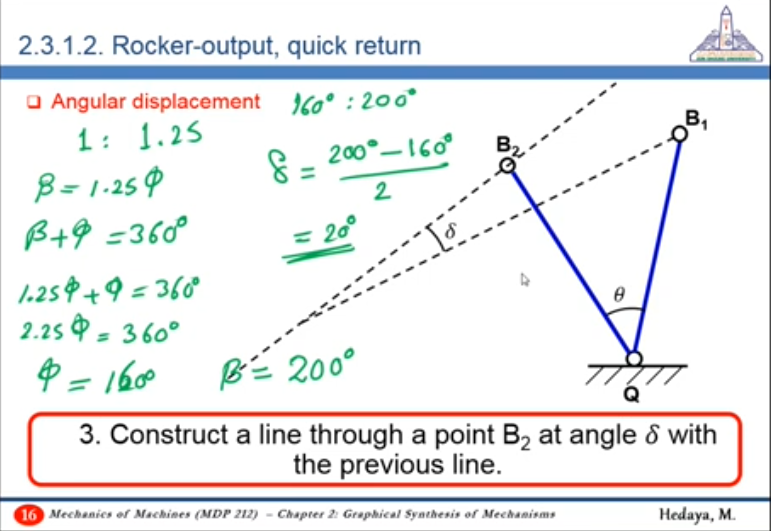
Why is the difference between the larger angle and the smaller angle equal to ?
needs a to be 180
is larger than 180 by
So needs another to be as
If , , return = go
Two extreme positions coincide on each other
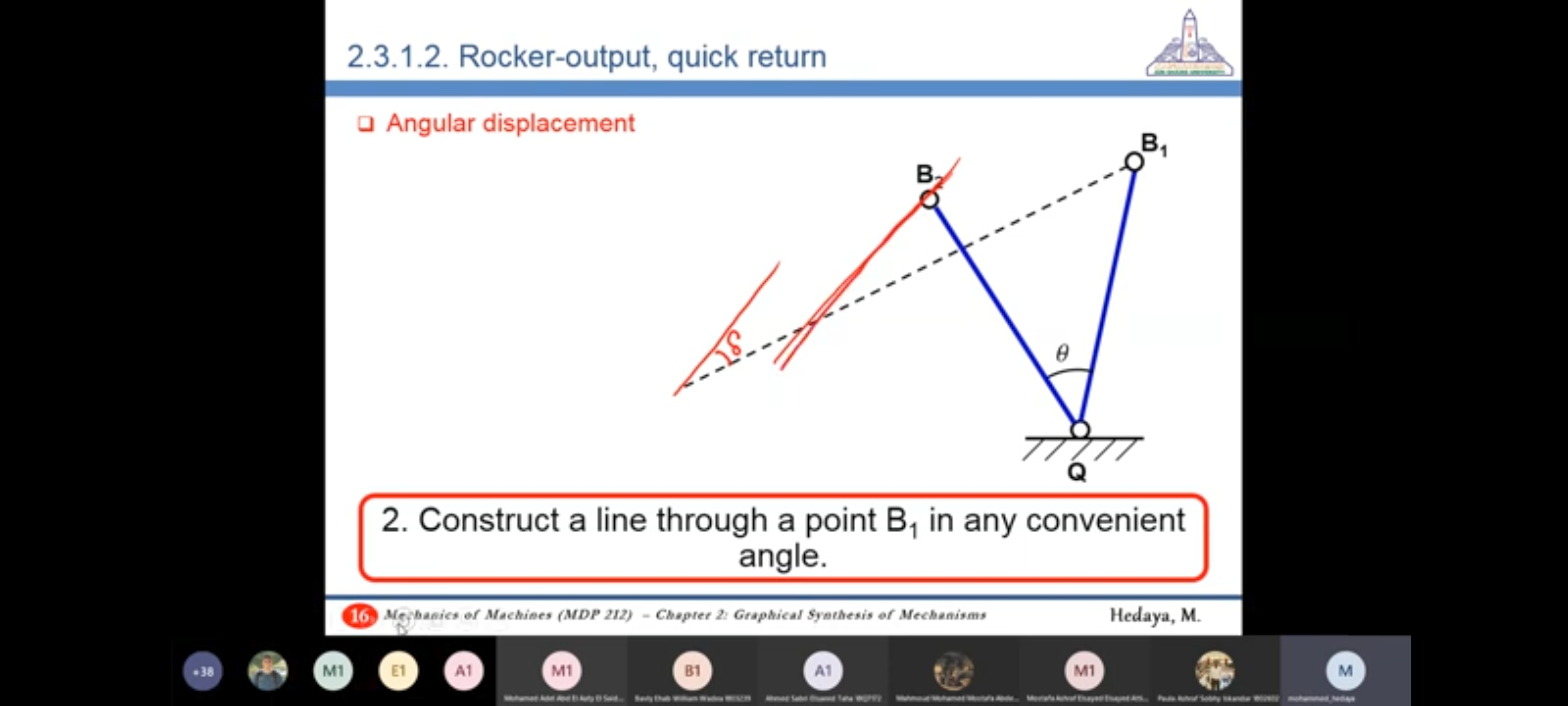
Note: Quick-return ratio can be used for Positional Analysis (see problem 1.7 in Sheet 1) and Synthesis of Mechanisms (e.g. Rocker-output, quick return) as well
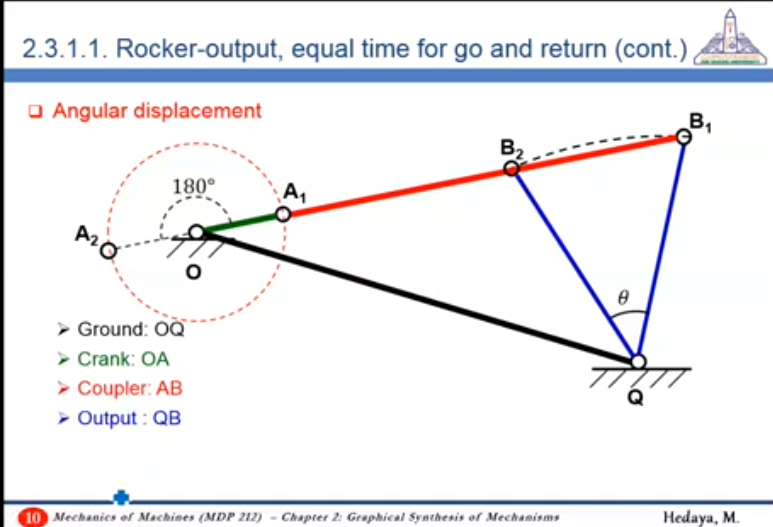
48:56 Rocker-output, equal time for go and return - Angular Displacement - Required: Angular Displacement
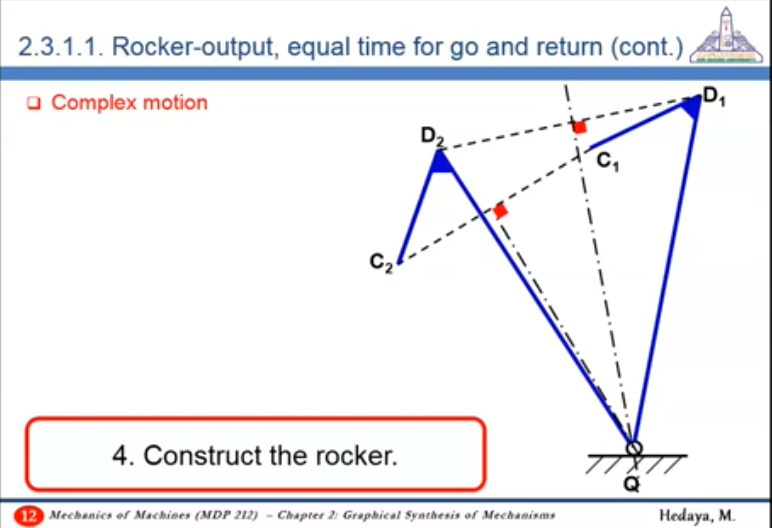
54:41 Rocker-output, equal time for go and return - Complex motion - Required: Complex motion
- General Plane Motion ⇒ Rotational Motion about a fixed point
- Finding center of an arc
- B is lower pair
To make the motion happen in equal time:
Note: blue rectangle = one rigid link
How to calculate ?
How was the radius of crank obtained in this way?
Crank + Coupler = OB1 Coupler - Crank = OB2
How to draw rocker?
- Draw a line with angle between the locus of hinge of the crank (O)
- Draw a line that is parallel to that line and intersects with B2