- Space mechanism
- Gear box to back axel → Two Hooke’s joints
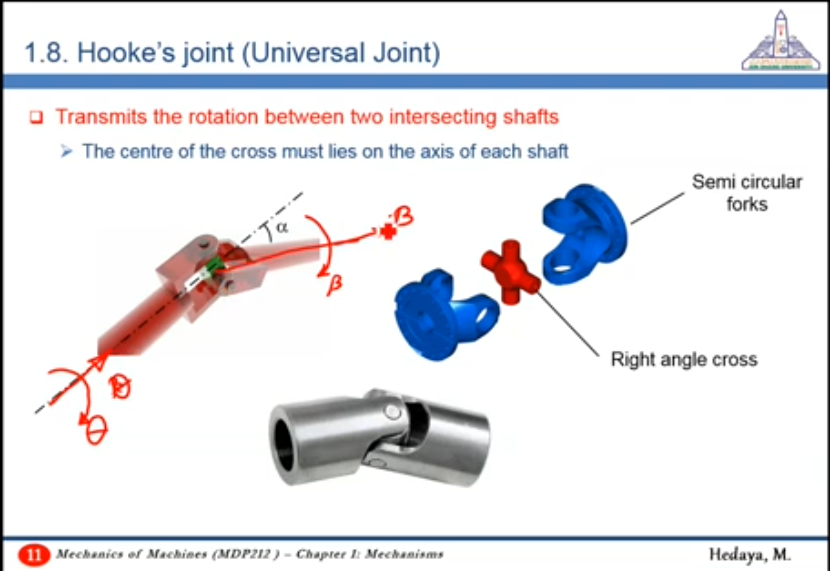
- The inclination between the shafts leads to a difference between their angular velocities
- The cross allows for the rotation of the inclined shafts, but leads to the difference in their angular velocities due to the resolution of the angular displacement vector
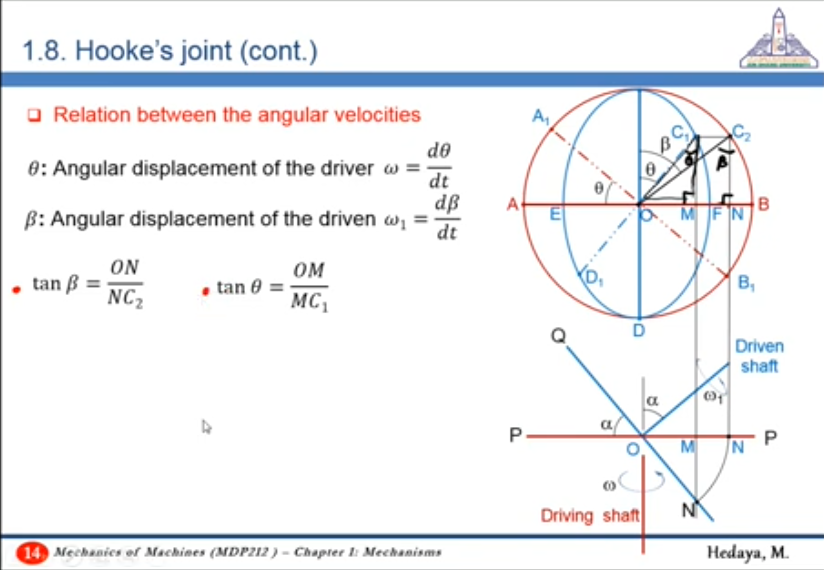
32:40 Mathematical Relation between the angular velocities
- Apply projection rules on the two planes of rotation of the shafts to derive the relation
00:05 Follow Mathematical Relation between the angular velocities
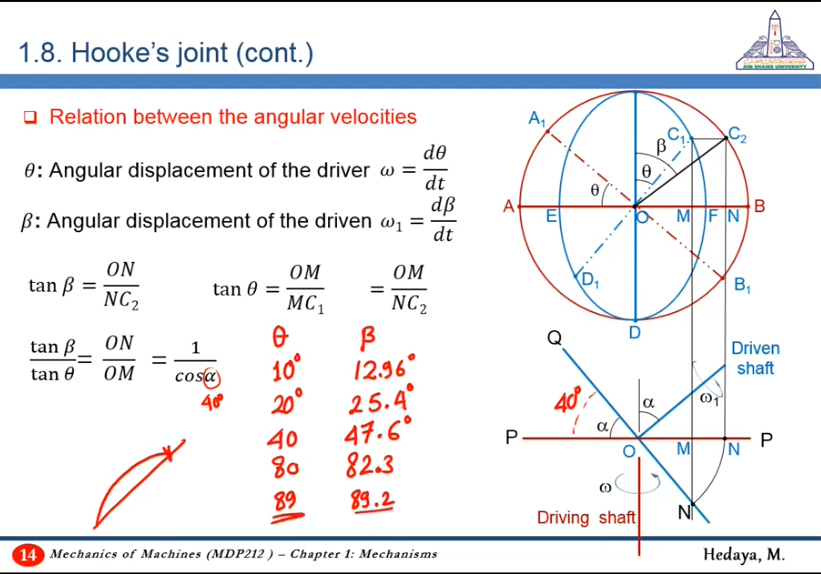
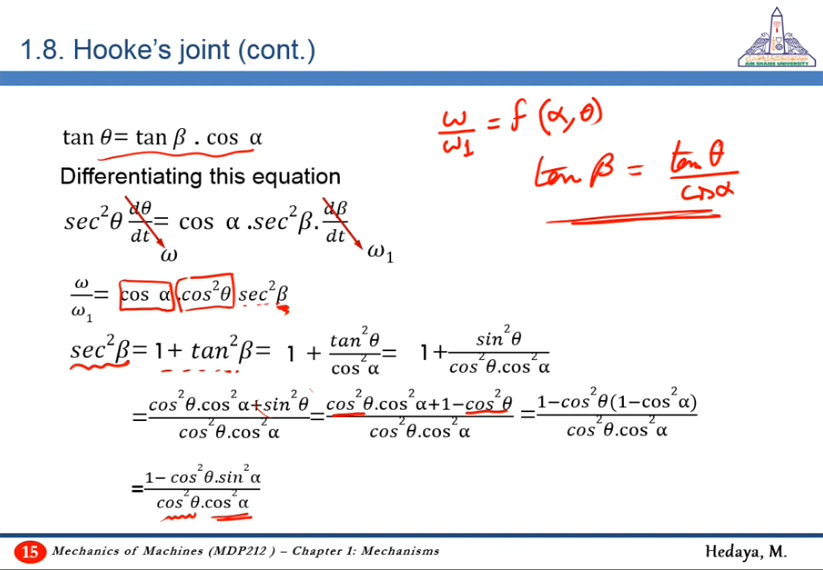
- Obtaining a relation between angles
- Differentiating wrt time to get a relation between angular velocities
- Cleaning the relation to be a function of (1) inclination angle between the two shafts and (2) angular displacement of driving shaft
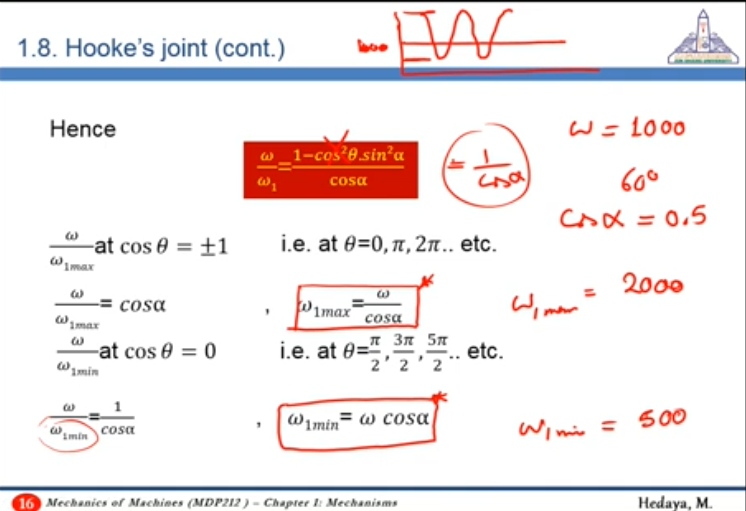
Final result:
10:56 How to measure in Relation between the angular velocities?
At initial time:
- Fork of input shaft is on the plane of the two shafts
- Fork of output shaft is on a plane normal to the plane of the two shafts
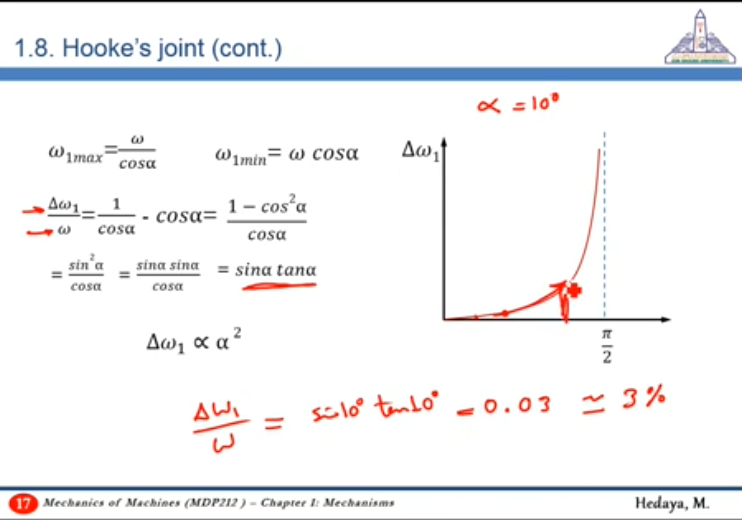
12:22 Understanding fluctuation using Relation between the angular velocities
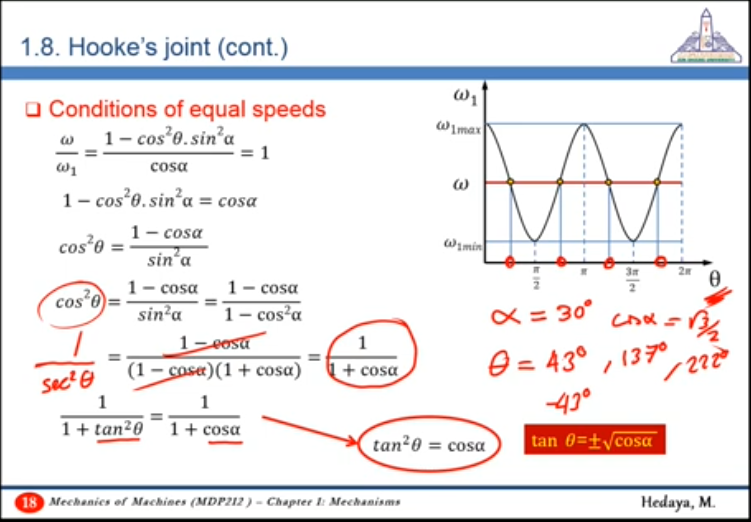
To better understand fluctuation, it is better to relate it to the mean speed (speed of driving shaft) and express it as a percentage of it
- as increases, fluctuation increases
Using :
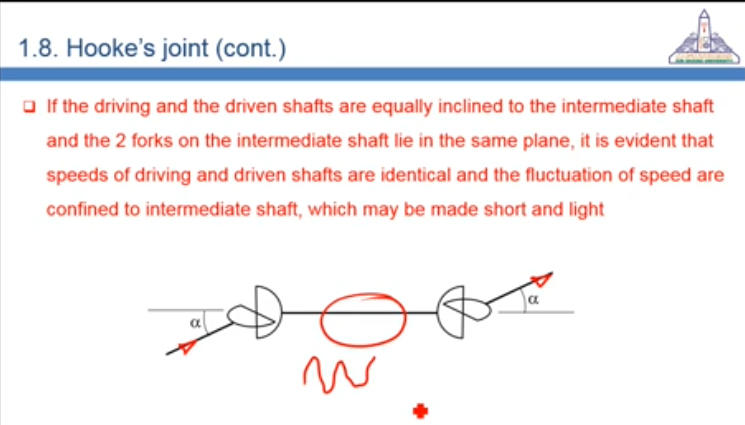
28:11 Using multiple Hooke’s joint (Universal Joint) to transmit motion between two parallel shaft's
By ensuring that the forks of the intermediate shaft are assembled on the same plane, fluctuations at on joint of the shaft are eliminated at the other joint, limiting the fluctuations to the intermediate shaft only
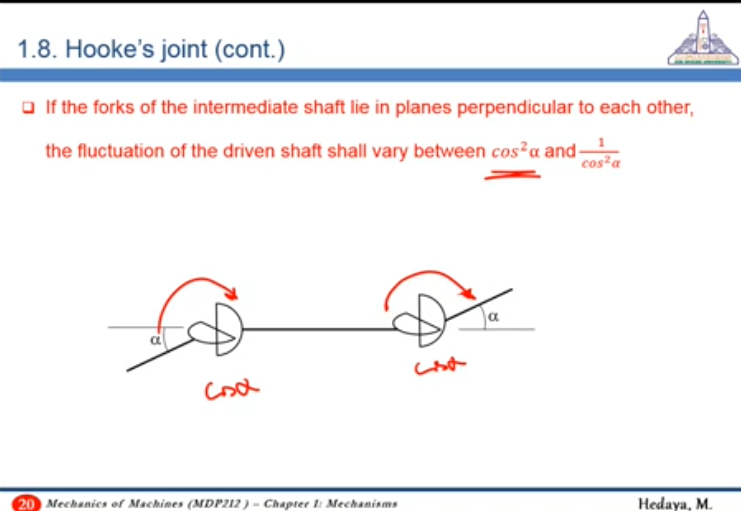
On the other hand, if the forks are assembled on planes perpendicular to each other, fluctuations at on joint are amplified at the other joint